Goals
- JIRA: CDAP-3969: CDAP should offer a temporary location to store results between jobs of a workflow.
- JIRA: CDAP-4075: Error handling for Workflows.
Checklist
- User stories documented (Sagar)
- User stories reviewed (Nitin)
- Design documented (Sagar)
- Design reviewed (Albert/Terence/Andreas)
- Feature merged (Sagar)
- Examples and guides (Sagar)
- Integration tests (Sagar)
- Documentation for feature (Sagar)
- Blog post
Use Cases
- JIRA: CDAP-3969: CDAP should offer a temporary location to store results between jobs of a workflow.
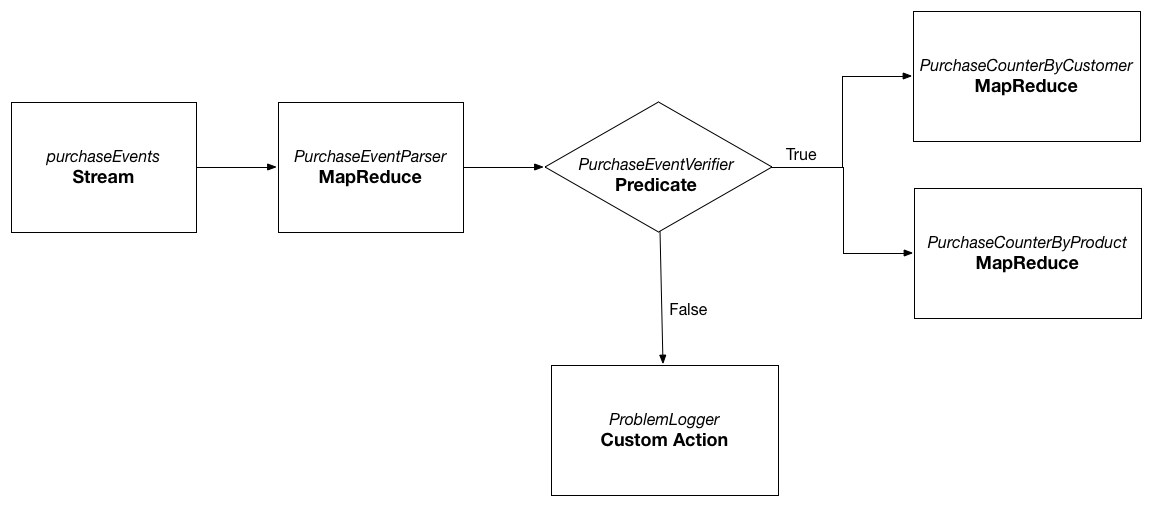
Case A)Consider the above sample workflow from CDAP-Workflow guide. The goal is to process the raw purchase events from the purchaseEvents stream and find the purchases made by each customer and purchases made for the particular product. When workflow runs, PurchaseEventParser reads the raw events from the purchaseEvents stream and writes the purchase objects to the purchaseRecords dataset. This dataset is later used by PurchaseCounterByCustomer and PurchaseCounterByProduct MapReduce programs as input to create the datasets customerPurchases and productPurchases respectively. Note that when the workflow completes, user is only interested in the final datasets that are created by the Workflow run: customerPurchases and productPurchases. The dataset purchaseRecords created by the MapReduce program PurchaseEventParser is temporary and no longer required when the workflow run is completed.
Case B)
MapReduce program in CDAP can output to the multiple datasets. Consider that the above Workflow can be modified, so that PurchaseEventParser can also write to the errorRecords along with the purchaseRecords dataset. The errorRecords contains the raw events from the purchaseEvents stream for which parsing failed. In this case, the errorRecords may not be temporary since user may want to perform some analysis on it using another CDAP application to find out the sources which are emitting the bad data frequently.Case C)
If for some reason, MapReduce program PurchaseEventParser is not generating the required amount of the data, user may want to keep the dataset purchaseRecords even after the run of the Workflow completes, so that he can debug it further. - JIRA: CDAP-4075: Error handling for Workflows.
Case A) When the Workflow fails for some reason, user may want to notify appropriate parties via email, possibly with the cause of the failure and the node at which the Workflow failed.
Case B) When the Workflow fails for some reason at a particular node, user may want to cleanup the datasets and files created by the previous nodes in the Workflow.
User Stories
- As a developer of the Workflow, I want the ability to specify that the output of the particular dataset used in the Workflow is temporary for that particular run, so that Workflow system can clean it up after the run completes. (CDAP-3969)
- As a developer of the Workflow, I should be able to specify whether the temporary datasets created by the Workflow run should be deleted or not after the Workflow run finishes. This way I can do some debugging on the temporary datasets once the Workflow run is failed. (CDAP-3969)
- I want the ability to delete the temporary datasets generated for the particular Workflow run, if I chose to not delete them after the Workflow run finishes. (CDAP-3969)
- MapReduce program can output to multiple datasets. As a developer of the Workflow, I want the ability to selectively specify some of the output datasets of the MapReduce program as transient inside Workflow. (CDAP-3969).
- I should be able to specify whether to keep the transient dataset even after the Workflow run is finished. (CDAP-3969)
- I should be able to make the non-transient dataset as a transient for the particular run of the Workflow. (CDAP-3969)
- As a developer of the Workflow, I want ability to specify the functionality(such as sending an email) that will get executed when the Workflow finishes successfully. (CDAP-4075)
- As a developer of the Workflow, I want ability to specify the functionality(such as sending an email) that will get executed when the Workflow fails at any point in time. I want access to the cause of the failure and the node at which the workflow failed. (CDAP-4075)
Approach for CDAP - 3969 (WIP)
Consider again the Workflow mentioned in the use case above.
In above Workflow, the datasets errorRecords, customerPurchases, and productPurchases are non-transient datasets. They can be defined inside the application as -
public class WorkflowApplication extends AbstractApplication { ... // define non-transient datasets createDataset("errorRecords", KeyValueTable.class); createDataset("customerPurchases", KeyValueTable.class); createDataset("productPurchases", KeyValueTable.class); ... }Since purchaseRecords is the dataset local to the Workflow, it can be defined inside the Workflow configurer method as -
public class PurchaseWorkflow extends AbstractWorkflow { @Override protected void configure() { setName("PurchaseWorkflow"); ... // create the Workflow local datasets here - createLocalDataset("PurchaseRecords", KeyValueTable.class); ... addMapReduce("PurchaseEventParser"); ... } }- When the application is deployed, following datasets are created - errorRecords, customerPurchases, and productPurchases
- If MapReduce program PurchaseEventParser is ran by itself, outside the Workflow, it would fail, since the purchaseRecords is not defined in the application scope. Its user's responsibility to make sure that the dataset exists in the correct scope.
User can choose to not to delete the local dataset even after the Workflow run is complete by specifying the runtime argument.
// To keep the Workflow local purchaseRecords dataset even after the Workflow run is completed following runtime argument can be specified - dataset.purchaseRecords.keep.local=true // In order to keep all the local datasets even after the Workflow run is completed following runtime argument can be specified - dataset.*.keep.local=true
- WorkflowDriver will thus get the multiple pair of <MapReduceProgram, TransientDataset>. WorkflowDriver can then pass this information to the MapReduceProgramRunner.
- MapReduceProgramRunner will create the transient dataset instances with unique names. For example if the dataset name is purchaseRecords, its corresponding transient dataset could be created with name purchaseRecords.<mapreduce_runid>.
MapReduceProgramRunner while creating the BasicMapReduceContext can pass on this dataset name mapping (for example in this case <purchaseRecords, purchaseRecords.xyzzz>) to it. All calls to the MapReduceContext.addOutput will be intercepted, so that if they are for the transient datasets, then the name of the dataset will be replaced by the transient dataset name.
class BasicMapReduceContext { // Map from dataset's actual name to the internal unique transient name private final Map<String, String> transientDatasetNameMapping; public BasicMapReduceContext(Program program, RunId runId, Arguments runtimeArguments, MapReduceSpecification spec, ... /* MapReduce program can have multiple transient datasets as output*/ Map<String/*dataset name*/, String/*transient dataset name*/> transientDatasetNameMapping) { ... // Store the transient dataset name mapping this.transientDatasetNameMapping = transientDatasetNameMapping; ... } @Override public void addOutput(String datasetName, Map<String, String> arguments) { String transientDatasetName = transientDatasetNameMapping.get(datasetName); // It is possible that the arguments here are scoped by the name of the dataset. // For example dataset.purchaseRecords.cache.seconds=30. // We will need to add the scoped parameters under the name of the new transient dataset // as dataset.purchaseRecords.<mapreduce_runid>.cache.seconds=30 addOutput(datasetName, new DatasetOutputFormatProvider(datasetName, arguments, getDataset(datasetName, arguments), MapReduceBatchWritableOutputFormat.class)); } @Override public void addOutput(String outputName, OutputFormatProvider outputFormatProvider) { String transientDatasetName = transientDatasetNameMapping.get(outputName); this.outputFormatProviders.put(transientDatasetName, outputFormatProvider); } }- BasicMapReduceContext is created in MapperWrapper and ReducerWrapper as well, so we will need to pass the mapping there using the MapReduce job configuration.
- Once the Workflow run completes, the corresponding transient datasets can be deleted from the WorkflowDriver.