Goals
Explore CDAP Entities in Hue
Use Hue's admin interface to manage ACL for CDAP stored in Apache Sentry
Checklist
- User stories documented (Shenggu)
- User stories reviewed (Nitin)
- Design documented (Shenggu)
- Design reviewed (Andreas)
- Feature merged (Shenggu)
- Integration tests (Shenggu)
- Documentation for feature (Shenggu)
- Blog post (Shenggu)
User Stories
- As a Hue admin, I should be able to easily configure CDAP as a plugin app in the Hue system
- As a CDAP user or a CDAPadmin, I should be able to explore all the entities of CDAP (ex: Namespaces, Streams, Programs etc.) in Cloudera Hue's UI.
- As a CDAP user, I should be able to perform all the ACL management operations provided by Apache Sentry through Cloudera Hue's admin UI.
- CDAP superusers can manage all the rules
- A user/groups who have ADMIN on one entity can give ACL on that entity to other users/groups
Design
The system utilize the Cloudera Hue's interface to manage the access control configuration between CDAP and Apache Sentry. The Hue itself does not store any state during this process.
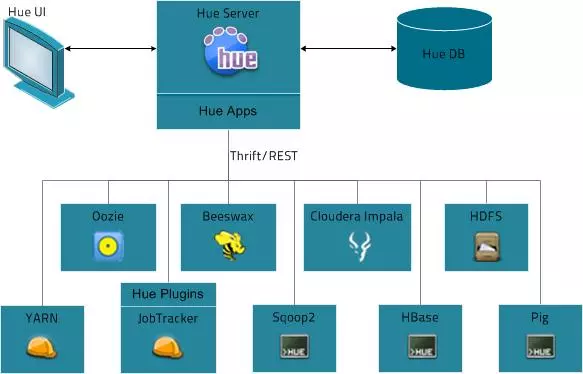
Brief Introduction of Cloudera Hue
(from hue's doc http://www.cloudera.com/documentation/archive/cdh/4-x/4-2-0/Hue-2-User-Guide/hue2.html)
| Hue is a set of web applications that enable you to interact with a CDH cluster. Hue applications let you browse HDFS and work with Hive and Cloudera Impala queries, MapReduce jobs, and Oozie workflows.
The Hue server part is written in python Django framework and different systems, say Hbase or Impala, are configured as separate apps in Django. The users are able to control these components on the cluster through the web interface. And it is also possible to add customized apps to Hue server to provide support for additional system.
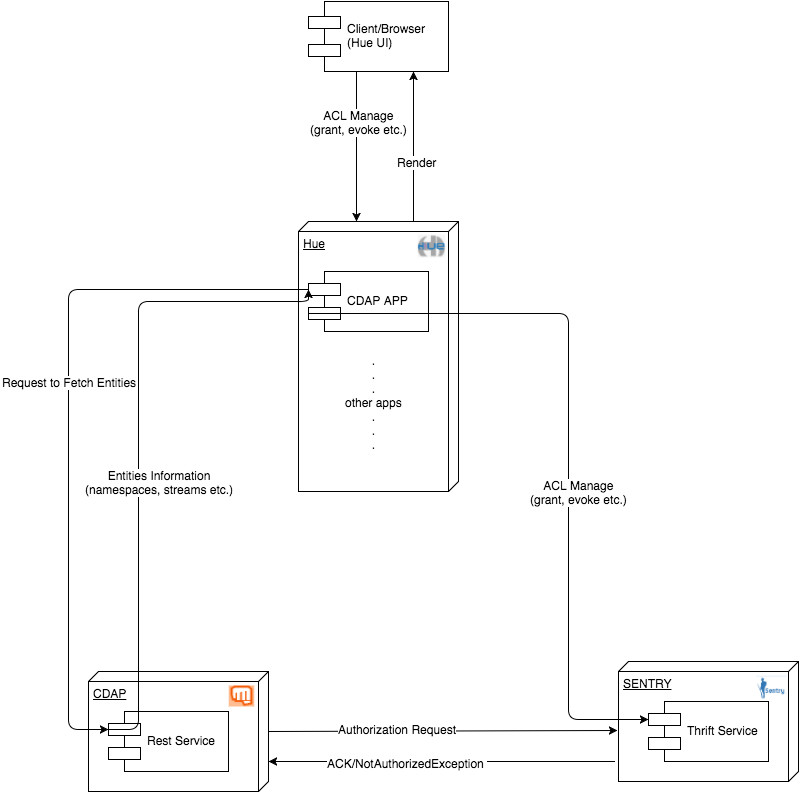
Logic view of the system
As shown in the above diagram, the CDAP and SENTRY support are configured as a plugin app installed in the Hue system. Hue's front system is implemented in Django, which provides good isolation and extension for multiple apps running together in a web service. A separate panel section will be created in the Hue's default UI for related operations. This app will communicate with the CDAP system through CDAP's restful api service. All the live entities will be displayed in Hue's UI. Communication with Apache SENTRY is enabled by SENTRY's thrift service. When admin grants/ evokes certain privileges through the Hue UI, it will be propagated to the SENTRY system and take effects on the further request coming from CDAP.
UI Mockup
One possible UI layout is shown below. All the entities in CDAP can be listed hierarchically in the left. When click on one specific entity, user is able to view the detailed properties of this entity and manage the acl rules associated with this entity. The actual UI may vary in colors and relative layout of elements but stick to this concept.
Configuration
To configure the CDAP app in HUE, simply copy the cdap app source code into $HUE_ROOT and run commands below:
$HUE_ROOT/tools/app_reg/app_reg.py --install cdap --relative-paths
and the setup script will automatically add all required fields into hue's configuration file.
Note: May move some customized settings into HUE's configuration (located in $HUE_ROOT/desktop/config.dist/hue.ini) when project moves on, i.e. root host address of CDAP's rest api etc.
Currently no specific configuration is required in CDAP side.
Routes
This section explain the routes defined in Hue's CDAP app. In Django (as Hue is written in Django), routes is named as urls.py that use regex to define the format. MAKO is used as the html template engine.
| URL | Response |
|---|---|
| GET /cdap/ | index.mako |
| GET /cdap/entity/entity_id/ | json of entity properties |
| GET /cdap/acl/entity_id/ | json of entity ACLs |
| POST /cdap/acl/add/entity_id/ --data {groupid, operation} | 200 ok |
| POST /cdap/acl/revoke/entity_id/ --data {groupid} | 200 ok |